Systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE, or simply lupus, is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system attacks its own tissue.
系统性红斑狼疮,SLE,或简称红斑狼疮,是一种自身免疫性疾病,身体的免疫系统会攻击自身组织。
Lupus is characterized by multisystem inflammation and production of auto-antibodies that bind to the body's own antigens.
红斑狼疮的特点是多系统炎症、产生大量的自身抗体结合自身抗原。
Inflammation and autoantibodies can cause damage to any organ, but most often affect the skin, joints, blood cells, kidneys, and brain.
炎症和自身抗体对任何器官都会造成损害,但最常影响的是皮肤、关节、血细胞、肾脏和大脑。
Lupus typically evolves in the form of recurrent episodes called flares, followed by periods of partial or complete remission.
通常来说,红斑狼疮病情呈反复发作,这种症状被称为“耀斑”,随后是部分或完全缓解。
Symptoms vary depending on the body system that is affected, and may include: fatigue, fever, or headache; joint pain, joint stiffness or muscle pain;
症状因受影响的身体系统而异,可能包括:疲劳、发烧或头痛;关节疼痛、关节僵硬或肌肉疼痛;
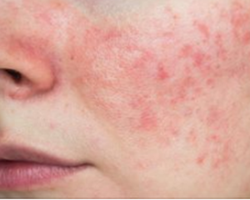
skin rash, in particular a butterfly-shaped rash on the face known as "malar rash"; or rash that appears or worsens when exposed to sunlight;
皮疹,特别是脸上的蝴蝶状皮疹,称为“颊疹”;或暴露在阳光下出现或恶化的皮疹;
symptoms of anemia, shortness of breath, or chest pain; confusion or memory loss; nausea, or abdominal pain; and urinary symptoms.
贫血、呼吸短促或胸痛的症状;混乱或失忆;恶心或腹痛;还有泌尿系统症状。
Lupus is typically diagnosed between 15 and 45 years of age.
红斑狼疮通常会在15到45岁之间被诊断出来。
The condition occurs more often in people of African, Hispanic, or Asian origins, and is much more common in women than in men.
这种病症更常见于非洲人、西班牙人或亚洲人,女性比男性更常见。
Lupus has a significant genetic component.
遗传成分在红斑狼疮的发病中占有很重要的地位。
A large number of genes have been linked to the disease predisposition, with most of the genes having a role in the functioning or regulation of the innate or adaptive immune response.
大量基因与疾病易感性有关,其中大多数基因在先天或适应性免疫反应的功能或调节中起作用。
Evidence points to dysregulated apoptosis, which leads to increased cell death in lupus patients.
有证据表明,细胞凋亡紊乱导致红斑狼疮患者的细胞死亡增加。
Fragments of dead cells are then presented to the immune system.
死亡细胞的碎片随后被呈递给免疫系统。
In a healthy immune system, these self-antigens are usually ignored,
在健康的免疫系统中,这些自身抗原通常会被忽略,
but in lupus patients, genetic defects may result in formation of intolerant lymphocytes that react to the body's own antigens.
但在红斑狼疮患者中,遗传缺陷可能导致形成对自身抗原有反应的不耐受淋巴细胞。
This causes aberrant activation of auto-reactive B- and T-cells, leading to production of autoantibodies and inflammatory factors.
这会引发自身反应性B细胞和T细胞的异常激活,导致自身抗体和炎症因子的产生。
While genetic factors underlie the background mechanism, the disease itself is typically triggered by environmental factors such as infections, drugs, or exposure to sunlight.
虽然遗传因素是背景机制的基础,但这种疾病本身通常是由感染、药物或暴露在阳光下等环境因素引发的。
Because of the wide range of possible symptoms, diagnosis of lupus is challenging.
由于红斑狼疮可能出现的症状范围很广,因此诊断具有挑战性。
Diagnostic tests aim to detect autoantibodies and identify the affected systems, and may include: autoantibody tests, complete blood count and other blood tests, kidney function tests,
诊断测试旨在检测自身抗体并确定受影响的系统,可能包括:自身抗体测试、全血细胞计数和其他血液测试、肾功能测试、
liver function tests, imaging studies for joints, heart, lung, or brain, and biopsy sampling for skin, kidneys, joints or nervous system.
肝功能检查,关节、心脏、肺或脑的影像学检查,皮肤、肾脏、关节或神经系统的活检取样。
Treatment depends on the system that is affected, but most patients are treated with medications that reduce inflammation or modify the immune system.
治疗方法取决于受影响的系统,但大多数患者都会接受减少炎症或修改免疫系统的药物治疗。
These include: hydroxychloroquine, corticosteroids, non-biologic and biologic immuno-suppressants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
这些药物包括:羟氯喹、皮质类固醇、非生物和生物免疫抑制剂以及非甾体抗炎药。


